Key Considerations in Choosing Between Spherical Head Anchors and Offset Variants
Load-Bearing Capacity in Precast Lifting Applications
Spherical head anchors and offset spherical head anchors are both integral to precast lifting systems, but they differ in their load-bearing behavior. The axial and shear capacities depend on the anchor size, embedment depth, and concrete strength. Typically, spherical head anchors offer a balanced performance under axial loads due to their symmetric design, while offset variants may deliver improved shear resistance in certain configurations due to their geometry.
The load performance of any lifting anchor is directly influenced by the compressive strength of the concrete during lifting. For early-age lifting, choosing anchors like the offset type may compensate for lower concrete strength due to better load transfer angles.
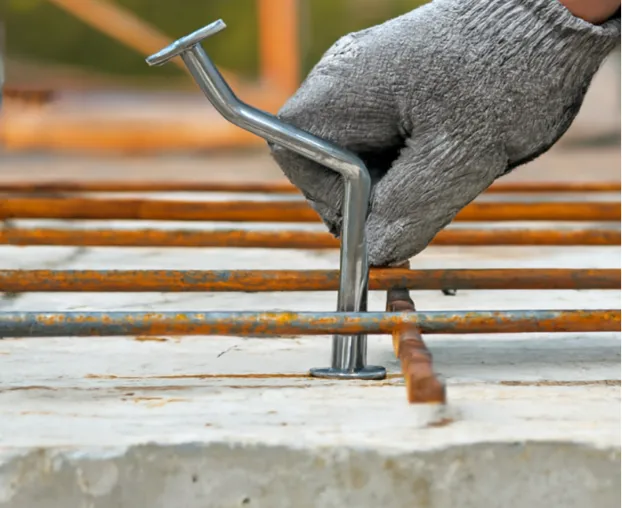
Anchor geometry also plays a role in distributing stresses throughout the concrete. In lifting scenarios, the symmetrical form of spherical head anchors helps maintain uniform load paths, which is particularly beneficial in vertical lifts.
Anchor Length, Size, and Concrete Embedment Depth
The size and length of anchors not only determine how deep they must be embedded but also affect how efficiently loads are transferred. For instance:
| Anchor Type | Size (T) | Length (mm) | Typical Embedment |
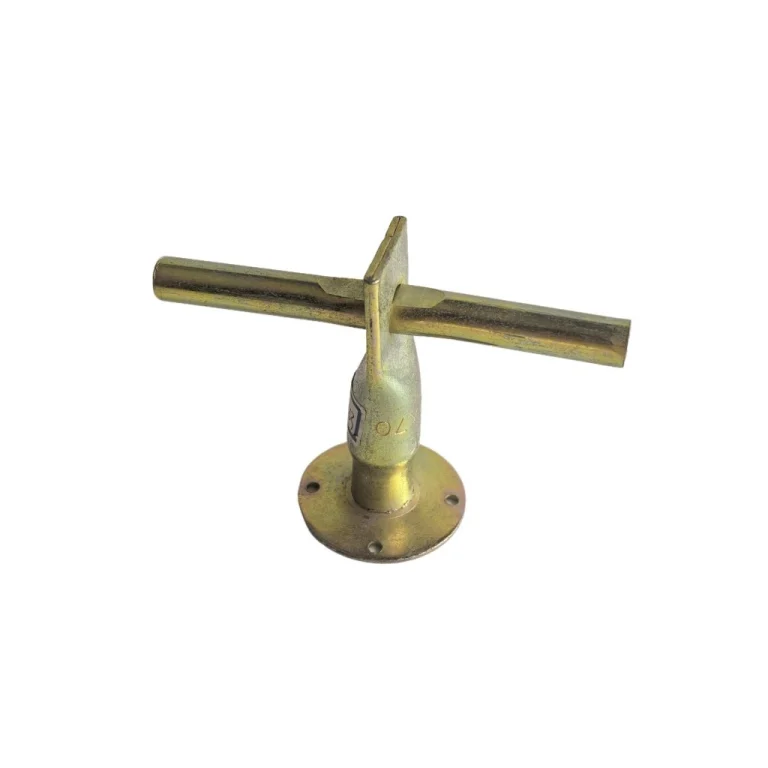
| Spherical Head | 5T | 120 | Moderate |
| Offset Anchor | 5T | 240 | Deeper |
Longer offset anchors require deeper embedment which may be restrictive in thin panels or walls. This is especially relevant when edge distances are tight or reinforcement congestion is high. Choosing a compact spherical head anchor could avoid interference with rebar.
Lifting Angle and Directional Load Behavior
Lifting angle dramatically impacts the anchor’s behavior. When lifting at angles beyond 30°, spherical head anchors tend to lose efficiency unless appropriately reinforced. Offset anchors, due to their shifted load axis, accommodate angled pulls better, reducing stress concentrations.
Design tolerances for multi-directional loads should be verified. If tilting or rotation occurs during lifting, offset anchors may offer higher safety margins due to more favorable lever arm mechanics.

Compatibility with Lifting Equipment and Site Conditions
Lifting Clutch Compatibility Across Anchor Types
Not all lifting clutches are universal. BaoQi offers a wide range of lifting eye clutches (e.g., JLC050 for 3-5T) compatible with both spherical and offset anchors. However, some offset variants may require customized clutches with specific locking profiles.
In terms of operation, spherical head systems often allow for quicker engagement and disengagement thanks to their centered design. Offset systems might introduce minor alignment challenges during frequent use.
Adaptability to Varying Concrete Strengths on Site
Construction timelines don’t always allow full curing before lifting. Anchors must be matched with expected concrete strength at the time of lift. Spherical head anchors generally require higher compressive strength for optimal performance. Offset types can sometimes better distribute loads across partially cured material—useful in modular building or disaster relief applications where speed is critical.
Corrosion Resistance Requirements in Harsh Environments
Both types can be finished with galvanization or stainless steel depending on exposure. For marine or freeze-thaw zones, BaoQi provides corrosion-resistant finishes to ensure long-term durability. Whether it’s for bridges or coastal structures, verifying surface treatment compliance with project specs is essential.
Standards Compliance and Quality Assurance Factors
Certifications Relevant to Anchor Selection Decisions
Anchor selection isn’t just about mechanical fit—it must align with international codes. Ensure compliance with applicable lifting anchor standards (e.g., EN 1992). Factory production control certificates and third-party test reports should be available from the supplier.
The Role of Manufacturing Quality in Anchor Performance
Forging versus casting makes a difference. BaoQi’s ISO‑9001 certified facilities ensure traceable production control. Forged parts tend to have superior grain structure and fatigue resistance—important under dynamic loads like tilts or drops.
Practical Applications and Engineering Trade-Offs in Anchor Selection
Installation Efficiency Across Precast Element Types
Time is money on-site. Spherical head anchors are faster to install with standardized recess formers and easy clutch access. Offset variants may need extra attention during setup due to their orientation-specific geometry.
- For thin wall panels: spherical head anchors are easier to place.
- For heavy beams or tilted elements: offset anchors may offer better alignment control.
Influence of Anchor Geometry on Concrete Placement and Vibration Flow
Anchor shape affects how concrete flows around it. Spherical heads minimize voids because their round profile allows better compaction during vibration. Offset heads can cause honeycombing if not correctly vibrated or if formwork tolerances are tight.
Balancing Safety Margins with Cost Efficiency in Project Planning
Every project juggles budget and risk. While spherical head anchors offer a proven track record and simpler logistics, offset types may provide better margins in complex lifts. The key is matching anchor type to the element’s function—walls vs stairs vs beams—and choosing based on actual load cases rather than generic specs.
Lifecycle costs also include labor time, clutch wear, and inspection needs. Consider total installed cost—not just unit price.
Integrating Supplier Capabilities into Engineering Decisions
Customization Potential Based on Project Requirements
For non-standard precast shapes or unique loading angles, customization is key. BaoQi offers custom forged solutions suitable for diverse installation contexts. Whether adjusting anchor length or modifying recess depth, having a responsive supplier streamlines design changes.
Supply Chain Reliability and Technical Support
Working with experienced manufacturers matters more than ever when deadlines are tight. Partnering with manufacturers like BaoQi ensures consistent quality across batches. Plus, their team can assist during the design phase—a major advantage when spec’ing anchors for new mold setups.
Long-Term Value Through Certified Production Processes
Finally, beyond unit cost is long-term confidence. BaoQi’s ISO‑9001 certified facilities ensure traceable production control. This consistency supports repeat orders and large-scale deployments without costly requalification or on-site issues.
Choosing between a spherical head anchor and an offset variant depends on more than just strength—it’s about geometry, site conditions, lifting strategy, and supplier partnership. By weighing these factors early in the project, engineers can make decisions that are safe, practical, and efficient.
FAQ
Q: Load-bearing differences between spherical head and offset anchors?
Spherical head: balanced axial loads via symmetry. Offset: better shear resistance and suited for angled/early-age lifts.
Q: When to choose spherical head anchors?
Ideal for thin panels, vertical lifts, tight edges, or when fast installation and uniform stress distribution matter.
Q: How do lifting angles impact these anchors?
Spherical head: efficient under 30° but less effective at higher angles. Offset: better for angled/multi-directional pulls.
Q: Embedment depth and size differences?
Spherical head (e.g., 5T: 120mm): moderate embedment, suits thin elements. Offset (e.g., 5T: 240mm): deeper embedment required.
Q: Lifting clutch compatibility?
Many clutches work with both, but offset may need custom profiles; spherical head allows faster engagement.