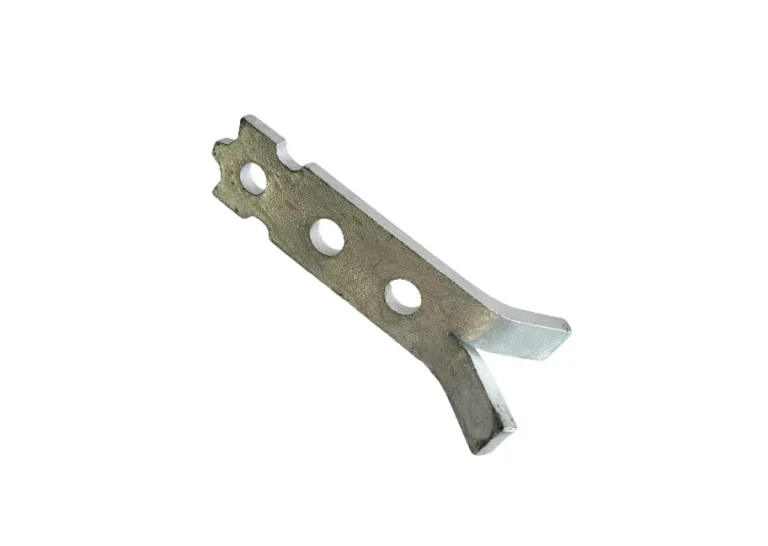
Spread anchors play a critical role in ensuring efficient load transfer within structural connections, particularly in precast concrete and steel reinforced systems. By optimizing how loads are distributed across the anchoring system, spread anchors enhance structural integrity, reduce stress concentrations, and increase the safety and longevity of buildings and infrastructure.
Their integration into modern construction practices reflects a strategic shift toward precision-engineered components that support both performance and safety.
Key Components of Spread Anchor Systems
Types of Spread Anchors Used in Structural Connections
Several types of spread anchors are available, each tailored to specific load conditions and installation requirements:
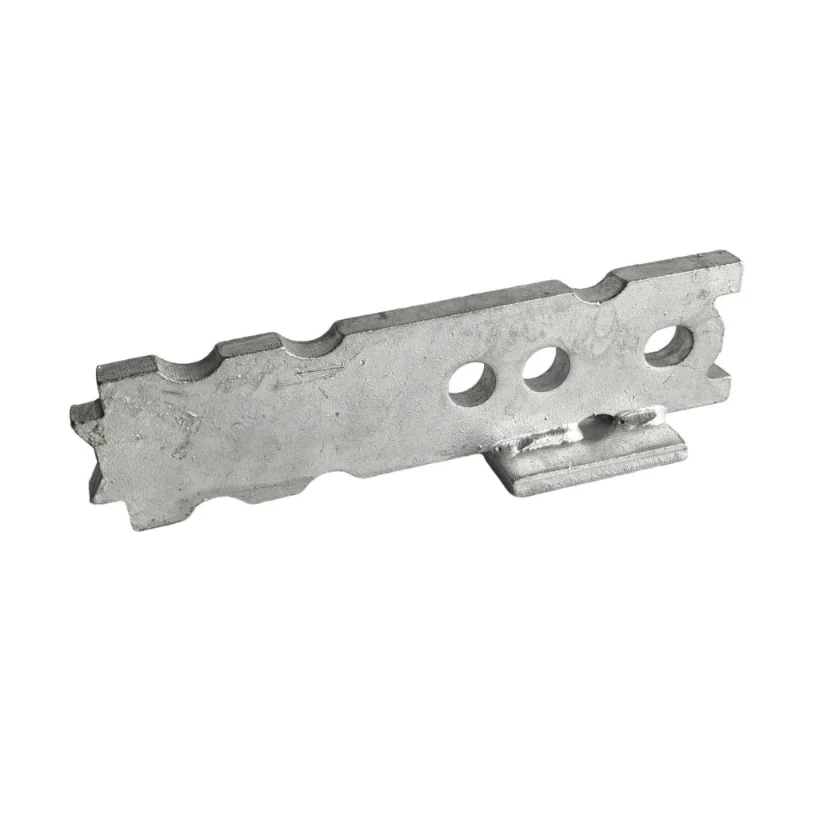
- Two hole spread anchors improve load distribution across wider surfaces, making them suitable for lifting thin or lightly reinforced panels.
- Flat foot and plate spread anchors provide stability during lifting and setting, especially in scenarios where secure footing is essential to avoid tilting.
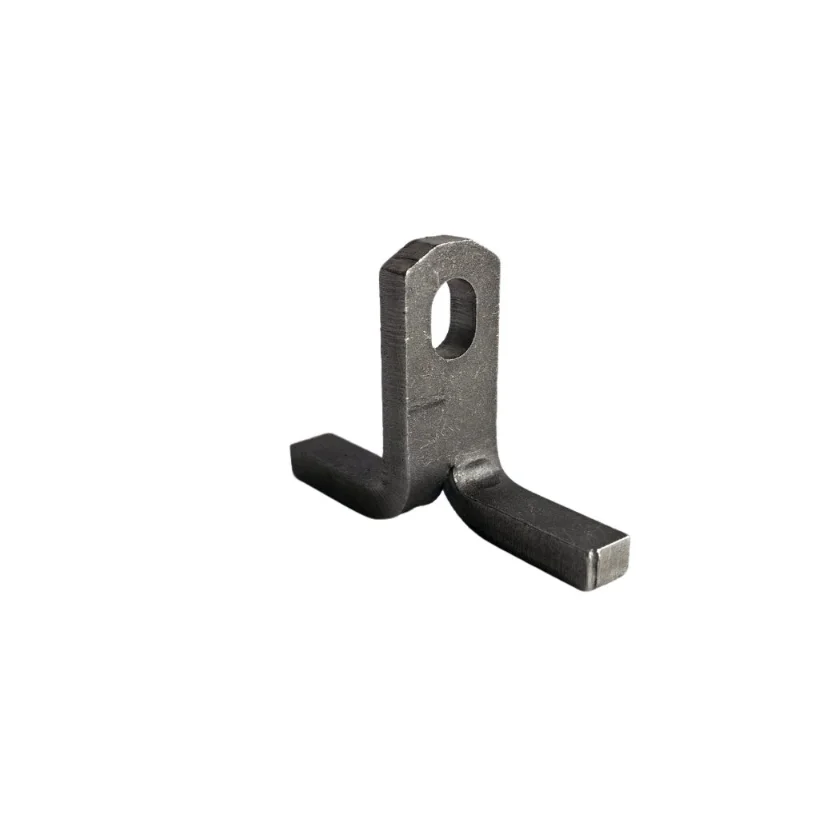
- Erection and unilateral erection anchors enable vertical alignment during installation, which is key in upright placement of panels.
These anchors range in capacity from 1.4T to 14T, as seen in items such as JSA014160 and JSA140370, offering flexibility across various concrete anchors applications.
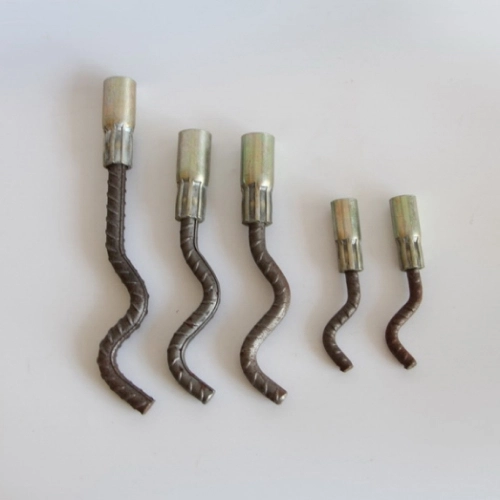
The Function of Rubber Recess Formers in Anchor Placement
Rubber recess formers are essential for accurate anchor positioning. Maintain precise positioning of anchors during concrete pouring is one of their primary benefits. This precision prevents misalignment that could compromise load paths.
Additionally, facilitate clean removal post-curing without damaging the concrete face ensures a neat finish and preserves the structural aesthetics of the panel surface.
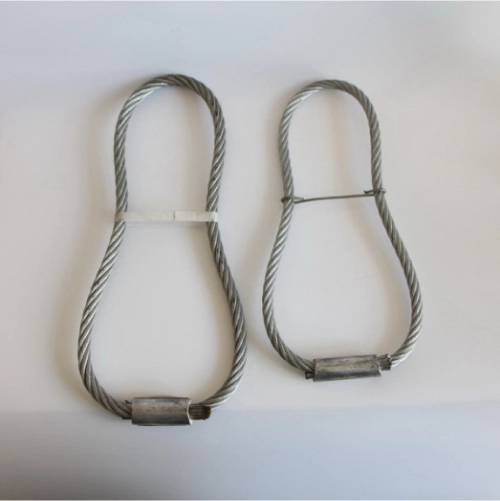
Role of Lifting Ring Clutches in Load Transfer
Lifting ring clutches ensure safe and consistent engagement between the lifting device and anchor. Secure engagement with anchor heads for controlled lifting prevents slippage under dynamic loads.
Furthermore, they allow for safe tilting and rotation of heavy elements without shifting anchor position, a capability especially valuable during complex installations involving steel structures or sloped placements.
Integration with Concrete Pouring Processes
Precasting Phase Considerations for Anchor Placement
Before pouring concrete, accuracy is everything. Anchors must be placed with millimeter-level precision:
- Accurate anchor alignment is essential for consistent load paths, ensuring that lifting forces are evenly distributed.
- Anchors must be embedded to correct depth to ensure full engagement post-pour. Depth miscalculations may reduce load capacity or create cracking risks.
Pouring and Curing Techniques That Support Load Efficiency
During the pour, managing flow rate is critical:
- Controlled pour rates reduce displacement or misalignment of anchors, keeping embedded parts stable.
- Curing schedules must account for anchor type to avoid stress cracking, especially for high-load spread anchors like JSA100370 or JSA140370.
Post-Curing Steps That Ensure Anchor Functionality
After curing, safety measures continue:
- Removing formwork without disturbing anchor orientation is critical to maintain the designed load path.
- Fitting and locking ring clutches must follow specific torque guidelines to ensure safety. Over- or under-tightening could compromise lifting performance.
Enhancing Load Transfer Through Design Optimization
Load Path Efficiency Enabled by Spread Anchors
Design geometry significantly impacts performance:
- Wide bearing surfaces reduce localized stress points in concrete members.
- Spread geometry helps redirect forces into compressive zones of the structure, minimizing tensile failure risks.
Minimizing Stress Concentration in Structural Connections
Stress distribution plays a pivotal role in durability:
- Evenly distributed loads lower the risk of cracking or premature failure.
- These systems are also compatible with both tension and shear force applications, offering broad usage scenarios across concrete pouring processes.
Performance Under Dynamic Loads and Tilted Installations
Spread anchors aren’t just for static loads:
- Tilt-up capabilities allow slabs to be lifted without tilting tables or forms.
- Dynamic response is improved through reinforced anchorage zones, ideal for seismic or high-vibration applications.
Comparing Spread Anchors to Alternative Lifting Systems
| Feature | Spread Anchors | Traditional Lifting Inserts |
| Load Capacity | High | Moderate |
| Embedment Depth Required | Reduced | Higher |
| Lifting Angle Flexibility | High | Limited |
| Stress Distribution | Even | Localized |
| Suitable for Tilt-Up | Yes | Often No |
Higher load ratings with reduced embedment depth requirements make spread anchors particularly attractive in modern construction workflows.
Widely used in precast wall panels, beams, columns, and staircases, these systems also suit modular construction where repeated lifts occur.
Safety Considerations During Installation and Use
Safe Handling Practices During Assembly and Lifting
Safety isn’t optional—it’s foundational:
- Proper training is required for rigging crews using ring clutch systems.
- Visual inspection protocols help detect wear or deformation before use.
Compliance with Industry Standards for Load Transfer Devices
To ensure long-term functionality:
- Must meet regional codes regarding embedment strength and pull-out resistance.
- Periodic testing ensures long-term reliability under service conditions.
Material Selection and Surface Treatment Strategies
Choosing Materials That Improve Anchor Durability
Material choices directly affect lifespan:
- High-grade forged steel offers superior tensile strength under load cycles.
- Corrosion-resistant coatings extend lifespan in exposed environments such as coastal or outdoor installations.
Surface Treatments That Enhance Performance
Coatings matter more than you think:
- Galvanization or epoxy coatings reduce degradation from moisture ingress.
- Heat treatment improves fatigue resistance under repeated loading conditions—a frequent demand in transportable precast systems.
Certification Protocols and Quality Assurance Measures
Testing Requirements for Load-Bearing Hardware
Before hitting the site, anchors undergo rigorous checks:
- Static load tests confirm rated capacities before deployment on-site.
- Non-destructive testing ensures internal integrity without damaging parts—a crucial step for high-capacity components like JSA140370.
Quality Control Processes During Manufacturing
Consistency begins at production:
- Dimensional checks ensure compatibility with formwork systems.
- BaoQi integrates multi-stage inspections to maintain consistent quality across batches.
Leveraging Expert Manufacturing Partnerships for Better Outcomes
Collaborating with Suppliers Who Understand Structural Demands
Working with knowledgeable partners matters. Working with experienced manufacturers ensures compliance with engineering specs. BaoQi’s familiarity with lifting anchor systems across multiple sectors offers peace of mind.
Long-Term Value Through Precision Engineering
Solid design equals fewer surprises down the road. Investing in well-designed anchoring systems reduces lifecycle maintenance. BaoQi’s focus on forged, cast, and stamped hardware solutions ensures long-term structural performance.
FAQ
Q1: What is the main advantage of using spread anchors over standard lifting inserts?
A: Spread anchors offer wider load distribution and require less embedment depth compared to traditional inserts.
Q2: Can spread anchors be reused?
A: While the anchors themselves remain embedded, accessories like clutches can be reused if properly inspected.
Q3: Are rubber recess formers necessary?
A: Yes, they ensure accurate placement and clean removal after curing.
Q4: What types of loads do spread anchors handle best?
A: They are effective under tension, shear, and dynamic tilt-up loads.
Q5: Does BaoQi offer custom anchoring solutions?
A: Yes, BaoQi supports custom fabrication tailored to specific project requirements.